We’re going WAY back for a history lesson today about some of the most well-known languages on Earth.
Latin was the language of the Roman Empire, but the classical Latin that was written was never the language of daily life. It was typically used for writings and formal documents within the Empire. And, it was certainly not the language soldiers and traders took with them to the edges of the Roman Empire when they were expanding and conquering!
Instead, the Romans spoke and wrote their own form of “graffiti”. Plainly speaking, they used a language much less polished than they used in their writings. The simplified Latin language of the common people is known as Vulgar Latin, because Vulgar is an adjective in Latin for the modern word “crowd." In other words, it was the people’s language, and it was much easier to understand than written Latin.
As the Roman Empire continued to grow and expand throughout the world, their language gradually changed depending on the region, and the region’s own dialect. Some of these changes included spelling, phonetics, sounds, and overall grammar.
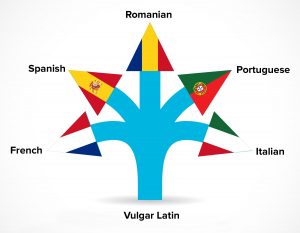
The languages that came from these changes are now known as the Romance Languages. Of all of the languages families in existence, the Romance languages group is likely the easiest to identify. These languages all came from Vulgar Latin in their own way, within historical times, and then turned into their own subgroup of the Italic branch of the Indo-European language family.
While many derivations of Romance Languages exist, the main ones that have stood the test of time and are still spoken today include:
- French
- Italian
- Spanish (the largest of the Romance Languages)
- Portuguese
- Romanian
These languages share a good portion of basic vocabulary and are still reasonably recognizable despite some phonological (sound pattern) differences, and spelling differences. They also share some similar grammatical forms.
However, romance languages differ quite significantly grammatically from their origins in Vulgar Latin. For example, although Latin had three grammatical genders (masculine, feminine, and neutral), the individual, modern Romance languages have only two (masculine and feminine).
Additionally, all Romance languages (except Romanian) have discarded the Latin scheme of six different cases for the noun, keeping only one case in use. As a result, the grammatical relationships of words are clarified mainly by prepositions and word order, instead of by inflections as they had been in Latin.
On the other hand, verbs in the Romance languages have preserved a highly developed conjugation system, which was inherited from Latin. This system of conjugation makes mood (formal or informal), number of individuals (me vs. we, you vs. you all) and tense exceptionally clear. That is one reason why learning verbs in the Romance Language is tricky and can be complicated for some.
A fun fact - in the year 2000, approximately 920 million people claimed a Romance language as their primary language, with around 300 million people having a Romance language as a second language! That is an incredible legacy that Vulgar Latin has had on modern society.
Do you need help translating a Romance Language? The Spanish Group can help! Learn about our services, and see how we can help you navigate the world of language today.

